Table of Contents
What Is Biometrics?
Biometric Technology is the statistical measurement and analysis of people’s unique physical and behavioural characteristics. The technology remains mainly used for identification and access control or the title of monitored persons. The simple principle of biometric authentication is that intrinsic physical or behavioural characteristics can accurately identify any person. The term biometrics remains derived from the Greek words bio (life) and metric (measure).
How Does Biometrics Work?
Authentication with biometric verification is increasingly used in business and public security systems, consumer electronics, and point-of-sale applications. Aside from security, the driving force behind biometric verification was convenience, as there is no need to remember passwords or carry security tokens around. Some biometric methods, such as a person’s gait measurement, can work without direct contact with the person to be authenticate.
The components of biometric devices are:
A reader or scanner for recording the biometric factor to be authenticated;
Software for converting the scanned biometric data to a standardized digital format and for comparing the match points of the observed data with the stored data; Yes
A database to steadily store biometric data for comparison.
Biometric data can be store in a centralized database. However, modern biometric implementations often rely on collecting biometric data locally and then having a cryptographic hash to perform authentication or identification without direct access to the data itself.
Types Of Biometrics
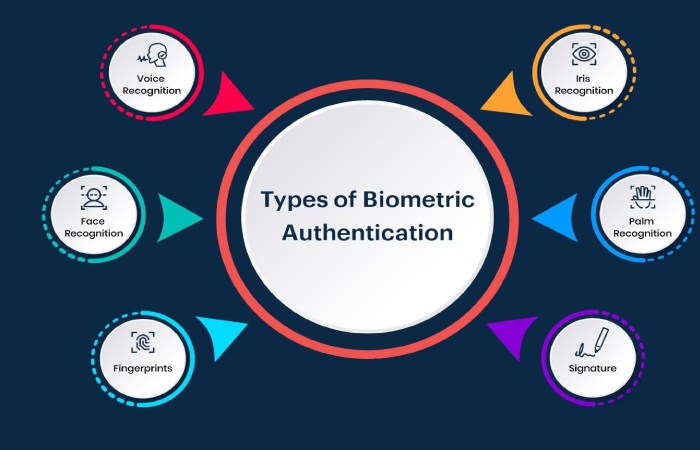
The two main types of biometric identifiers remain physiological traits and behavioural traits.
Physiological identifiers relate to the arrangement of the authenticating user and include the following elements:
- Face recognition
- Fingerprints
- Finger geometry (the size and position of the fingers)
- Iris recognition
- Vein detection
- Retinal scan
- Voice recognition
- DNA match (deoxyribonucleic acid)
- digital signatures
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Biometrics.
Using biometrics has many advantages and disadvantages regarding its use, security, and other related functions. Biometrics is beneficial for the following reasons:
- Unlike passwords, difficult to forge or steal;
- Easy and convenient to use;
- Generally the same throughout a user’s life;
- Not transferable; Yes
- Efficient because the models take up less storage space.
However, The Disadvantages Are As Follows:
- Commissioning a biometric system is expensive.
- If the system does not collect all of the biometric information, it may not be able to identify a user.
- Biometric databases can still be hacked.
- Errors like false rejections and false assumptions can always occur.
- If a user is injured, a biometric authentication system may not work; For example, if a user burns their hand, a fingerprint reader may not be able to identify them.
Examples Of Biometrics In Use
In addition to biometrics used in many smartphones today, biometrics is use in many areas. Biometrics is used, for example, in the following areas and organizations:
Respect the law
It is used in criminal identification systems such as fingerprint or palm leaf authentication systems.
United States Department of Homeland Security
It is use in border guards for many recognition, verification, and accreditation processes, such as electronic passport systems that store fingerprint data or facial credit systems.
Healthcare
It remains used in schemes such as national ID cards for identification and in health insurance programs that may use fingerprints for identification.
Airport Security
This field sometimes uses biometric data such as iris recognition.
However, not all organizations and programs will choose to use biometrics. For example, some forensic systems do not use biometrics to
Conclusion
TSA seeks to leverage Biometric Technology to automate the identity verification process to enhance security effectiveness, progress operational efficiency, and streamline the passenger experience while protecting privacy. TSA’s exploration of Biometric Technology is ideal for capitalizing on technological advancements in biometric system accuracy, speed, and ability to automate high-throughput operations.
Also Read: What Is Artificial Intelligence? – Work, Types, Uses, And More

